Ho Chi Minh University of Technology and Education (HCMUTE)
Hoang An Quoc & Huynh Nguyen Anh Tuan, Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology and Education, Vietnam
The introduction of Master programe of Chemical Engineering in Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology and Education began with the realisation of the Erasmus + program project “Future Oriented Chemistry – FOREST” from August 2023.
The main goal of the project is to improve the quality of Master programe towards green and sustainable development at partner universities.

Specific objectives of the project:
- Development of master’s programs of Chemical Engineering based on Future Oriented Chemistry;
- Improve capacity to develop Master’s training programs according to European standards.
- Develop transferable courses between member universities;
- Develop online courses;
- Teaching teachers new skills;
- Impact and change the thinking of stakeholders about future oriented chemistry.
- Creation of Excellence Center;
Needs for FOREST master program. The project team of HCMUTE together with Faculty of Chemical and Food Technology (FCT) has conducted a workshop with stakehoders including HCMUTE lecturers, lecturers from other universities, alumni, and enterprises to collect contributions and develop the Expected Learning Outcomes.
Outputs of the workshop. The results of the survey show that it is necessary to develop a Master’s programs of Chemical Engineering oriented towards green technology and sustainable development at HCMUTE. The Master’s program being developed at FCT needs to change the Learning Outcomes and courses to to meet the new requirements of modern education. The training program must focus on three elements: knowledge, skills and attitudes. In particular, there must be courses on engineering technology related to sustainable development.
The analytical data of the survey were used for developing learning outcomes of master program
Development of master program. The program has been developed within the framework of the European project Erasmus+ “Master programe of Chemical Engineering” with the participation of Linkoping University (Sweden), University of Leoben (Austria), Polytechnic Institute of Tomar (Portugal), Thai Nguyen University of Sciences (TNUS), Hue University of Sciences (HUS) and Vietnam National University of Forestry (VNUF).
The educational program has been developed under the state mandatory standard of postgraduate education of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Learning outcomes are formulated based on the European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS) guidelines.
Name of the programme: “Master programe of Chemical Engineering”
Code: 8.52.03.01
Number of ECTS credits for the programme: 120
Aim/purpose with the programme:
- The Master’s program in Applied Chemical Engineering aims to train high-quality human resources in the field of engineering technology to meet societal needs.
- It provides comprehensive knowledge and necessary skills to evaluate, analyze, and synthesize relevant factors to solve practical problems in chemical engineering.
- The program keeps students updated on new knowledge and technological trends in chemical engineering.
- Graduates are equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for significant roles in organizations, companies, universities, and research institutes in the field of Chemical Engineering. They are also prepared to continue their education for further advancement.
- Proficiency in English specialized in Chemical engineering technology and English communication in a multinational working environment.
Learning outcomes for the programme.
Learning outcomes of the program are described in Table 1.
Table 1. Programe Learning Outcomes
| Symbols | Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs) |
|---|---|
| I. | Knowledge |
| PLO1 | Evaluate basic and advanced knowledge to decide on solutions in production in the field of Chemical engineering. |
| PLO2 | Analyze technological processes and decide on key issues to improve technological processes in the field of chemical engineering. |
| II. | Skills |
| PLO3 | Ability to build an effective teamwork and demonstrate leadership. |
| PLO4 | Ability to analyze data and present scientific and technical results. |
| PLO5 | Proficiency in English specialized in Chemical engineering technology and communication in a multinational working environment. |
| III. | Attitudes |
| PLO6 | Awareness and appreciation of the importance of self-learning and the necessity of lifelong learning. |
| PLO7 | Recognition of the role of research and development. |
| PLO8 | Creative, responsible, and honest approach when carrying out research tasks. |
Content of the programme
The curriculum content of the Master’s degree is divided into five modules, which is done so according to the main focus of the program. The program’s courses are presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Content of the programe.
| Text | Number | Subjects | ECTS |
|---|---|---|---|
| I. General knowledge | 12 | ||
| PHIL | 530219 | Philosophy | 6 |
| RMTS | 530126 | Research Methodology and Theory of Science | 6 |
| II. Basic knowledge | 24 | ||
| AOCH | 533307 | Advanced Organic Chemistry | 6 |
| APHY | 534207 | Applied Physical Chemistry | 6 |
| PROM | 535907 | Project management | 6 |
| TOXC | 535607 | Toxicology | 6 |
| III. Professional knowledge | 42 | ||
| Compulsory | 18 | ||
| ESMD | 533907 | Energy storage materials and devices | 6 |
| BIRE | 534007 | Biofuels and renewable energy | 6 |
| AWRP | 535007 | Anti-degradation and improved weather resistance of polymer materials | 6 |
| Electives (select 24 ECTSs) | 24/114 | ||
| SOLC | 533207 | Solid-state Chemistry | 6 |
| MFHR | 536007 | Management of facilities and human resources | 6 |
| FHCP | 535107 | Fundamental of scale up in chemical processes | 6 |
| MSEL | 533707 | Material Selection | 6 |
| FINE | 535707 | Fine chemical engineering | 6 |
| CENA | 533807 | Catalytic Engineering and nanocatalysts | 6 |
| SPOL | 533407 | Structure and physio-chemical properties of polymers | 6 |
| MACE | 534307 | Modern analytical methods in chemical engineering | 6 |
| ASOC | 533507 | Advanced Statistical and Optimization in Chemical Engineering | 6 |
| APCH | 533607 | Advanced Polymer Chemistry | 6 |
| HERT | 535407 | Heterogeneous reaction technique | 6 |
| NANT | 534908 | Nanomaterial technology | 6 |
| CSSP | 535307 | Calculation and simulation of chemical structures and processes | 6 |
| CTNC | 534507 | Chemical technology of natural compounds | 6 |
| FCTE | 534607 | Fragrance and cosmetic technology | 6 |
| FIBT | 534707 | Fiber technology | 6 |
| ELPT | 534807 | Electrolysis and plating technology | 6 |
| DRUD | 535207 | Chemistry of drug delivery systems | 6 |
| CCHE | 535507 | Colorant chemistry | 6 |
| IV. Internship | 12 | ||
| INTE | 534407 | Internship 1 | 6 |
| INTE | 536107 | Internship 1 | 6 |
| IV. Graduation thesis | 30 | ||
| Total | 120 |
Module 1 (12 ECTS): General knowledge
It aims to provide a holistic overview of the history and philosophy of scientific development of science, issues related to the skills of conducting a scientific research.
Module 2 (24 ECTS): Basic knowledge
Basic knowledge module provides basic knowledge in Chemical engineering. This module provides basic knowledge in chemical engineering such as organic chemistry, physical chemistry, toxicology, as well as management skills.
Module 3 (18 Compulsory ECTS + 24 Elective ECTS) : Professional knowledge
Professional knowledge module provides specialized knowledge in the field of Chemical Engineering. In particular, students study 18 compulsory ECTS related to the field of green chemical technology and sustainable development. Students can then choose 24 out of a total of 114 ECTS according to their individual orientation.
Module 4 (12 ECTS): Internship
The module provides students with knowledge and skills to work in a corporate environment. Students can relate the theoretical knowledge they have learned in the training program with practical business knowledge. Students have the opportunity to consolidate specialized knowledge and develop necessary professional skills through group work activities and production activities at the enterprise. In addition, through the internship, students will demonstrate the role of an expert in controlling and handling chemical engineering problems.
Module 5 (50 ECTS): Master Thesis
The module provides students with the ability to solve a scientific and technical duty including: determining the scope of a topic, developing research methods, conducting research, collecting, analyzing and synthesize data to find a scientific and technical rule in the field of Chemical engineering. Finally, students are asked to explain research results in writing and speaking in a clear and logical methods.
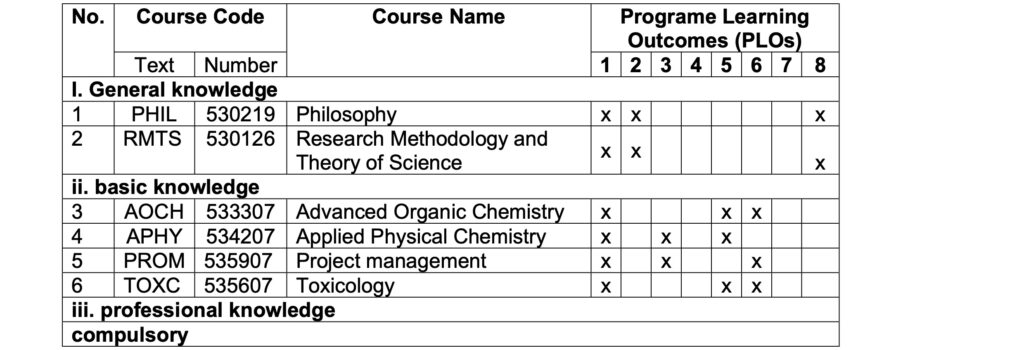
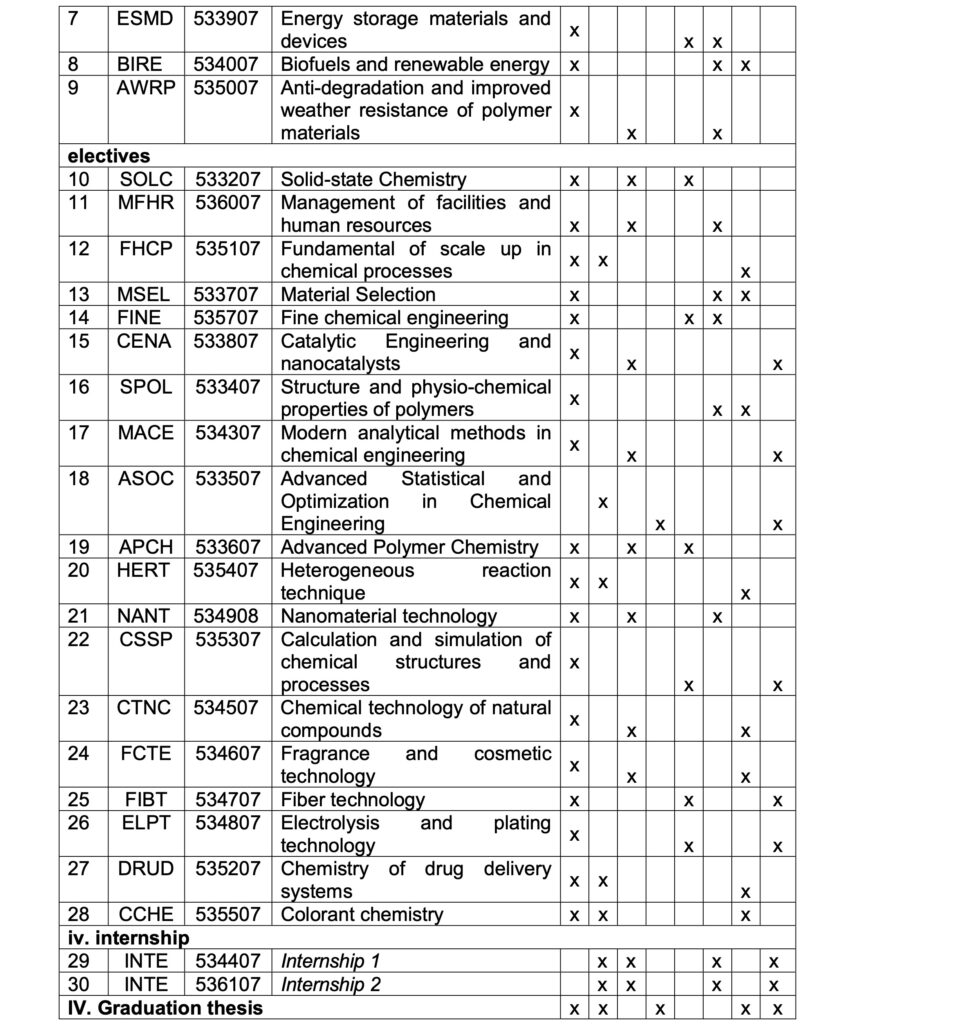
Mapping of PLOs and CLOs at the Master programe
The course curriculum determined the specific and measurable PLOs of the programme as shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Mapping of ELOs and CLOs at the CET programme
Online Courses
To facilitate student exchange between member universities when the Forest master program operates, the coordinators have directed HCMUTE to develop two online courses. The Department of Chemical Technology, Faculty of Chemical and Food Technology has developed two online courses including Applied Physical Chemistry and Advanced Organic Chemistry.
Online Course 1: Applied Physical Chemistry (6 ECTS, Compulsory)
Course Description: The course “Applided Physical chemistry” is designed to provide students with fundamental physical chemistry knowledge and its applications in multidisciplinary areas including phase diagram, smart polymers, and heat and electrochemical energy conversion and storage. Through this subject, students are able to read and understand phase diagrams, analyze and evaluate materials and technological processes. At the same time, students are also trained to develop critical thinking and the ability to use specialized English
Course objectives: The students are provided fundamental and applied physical chemistry knowledge in phase diagram, smart polymers and its applications, heat and electrochemical energy conversion and storage devices
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
CLO1. Acquire, evaluate, and integrate knowledge of physical chemistry in different practical applications as phase diagram analysis, phase change materials in thermal energy storage and conversion, smart polymers and their applications, and the fundamentals of electrochemistry and electrochemical energy storage devices.
CLO2. Able to use specialized English in reading scientific documents and presentations.
CLO3. Recognize and appreciate the importance of self-study and the need for life-long learning.
Content of Course:
- Chapter 1: phase diagrams and their applications
- Chapter 2: thermal energy conversion and storage using phase change materials
- Chapter 3: smart polymers and their applications
- Chapter 4. Fundamentals on electrochemistry and electrochemical energy storage devices
- Final seminar presentations.
Online Course 2: Advanced Organic Chemistry.
Course Description: This course is designed to provide students with knowledge about the reaction mechanism of organic synthesis reactions through experiments; techniques in organic synthesis; strategies and tactics in organic synthesis; IR, NMR, MS spectroscopy methods are used to determine the structure of organic compounds.
Course Objectives: The students are provides knowledge about the reaction mechanism of functional groups, C-C coupling reactions, and the mechanism of synthesis reactions of some intermediate functional groups in total synthesis; techniques in organic synthesis and organic synthesis process design, elucidate the structure of organic compounds using IR, NMR and MS spectroscopy methods.
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
CLO1. Present, explain, and analyze organic reaction mechanisms; and elucidate the chemical structure of organic compounds.
CLO2. Fluently use English terms in organic synthesis and structure elucidation using spectroscopic methods.
CLO3. Recognize and evaluate the important role of each step in the organic synthesis process, techniques and methods in organic synthesis, structure determination, thereby realize the importance and applications of organic synthesis.
Content of Course:
- Chapter 1: functional group modifications
- Chapter 2: Skeletal Modifications
- Chapter 3: The Techniques of Organic Synthesis
- Chapter 4: Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds