Hue University of Sciences (HUSC)
Tran Thi Ai My, Tran Anh Tuan, Nguyen Thi Ai Nhung, Hue University of Sciences, Vietnam
The introduction of the Master program of Chemistry at Hue University of Sciences began with the realisation of the Erasmus + program project “Future-Oriented Chemistry – FOREST” in August 2023.
The main goal of the project is to improve the quality of the Master’s program towards green and sustainable development at partner universities.

Specific objectives of the project:
- Development of the Master’s program of Chemistry based on Future-Oriented Chemistry;
- Improve capacity to develop a Master’s program in Chemistry according to European standards.
- Develop transferable courses between member universities;
- Develop online courses;
- Teaching new skills for teachers;
- Impact and change the thinking of stakeholders about future-oriented chemistry.
Needs for FOREST master program. HUSC’s project team together with the Science and Training Council of the Department of Chemistry met to agree on adding new subjects to increase awareness of climate change and prevention solutions, aiming to train human resources based on the future-oriented Chemistry.
The analytical data of the survey were used for developing learning outcomes of the master’s program
Development of master program. The program has been developed within the framework of the European project Erasmus+ “Master’s program of Chemistry” with the participation of Linkoping University (Sweden), University of Leoben (Austria), Polytechnic Institute of Tomar (Portugal), University of Catania (Italy), Thai Nguyen University of Sciences (TNUS), Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology and Education (HCMUTE) and Vietnam National University of Forestry (VNUF).
Name of the program: “Master’s degree of Chemistry”
Major: Chemistry
Code: 8440112
Education level: Master Degreee
Training Orientation: Applied
1. Objectives
The goal of a Master’s degree training program in Chemistry is to provide students with advanced and specialized knowledge in the field of chemistry, equipping them with the skills and expertise necessary for successful careers in academia, research, or industry. This program typically focuses on deepening understanding in core areas of chemistry such as organic, inorganic, physical, and analytical chemistry, while also fostering critical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and laboratory techniques. Through coursework, research projects, and hands-on experiences, students are challenged to explore the frontiers of chemical science and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their chosen area of specialization. Additionally, a Master’s degree in Chemistry aims to cultivate effective communication skills, ethical practices, and a commitment to lifelong learning, preparing graduates to make meaningful contributions to scientific research, innovation, and education.
1.1. General objectives:
– The general objective of a Master’s degree training program in Chemistry is to provide students with an advanced and comprehensive education in the various branches of chemistry.
– This includes a deepening of theoretical knowledge, development of practical laboratory skills, and exposure to cutting-edge research methodologies.
1.2. Specific objectives
– Advanced Knowledge: Provide students with advanced and specialized knowledge in key areas of chemistry, including organic, inorganic, physical, and analytical chemistry.
– Research Skills: Develop strong research skills, including the ability to design and conduct experiments, analyze data, and draw meaningful conclusions. Encourage students to contribute original research to the field.
– Specialization: Allow students to specialize in a particular sub-discipline of chemistry, such as biochemistry, environmental chemistry, materials chemistry, or medicinal chemistry, enabling them to become experts in a specific area.
– Critical Thinking: Foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills, challenging students to approach scientific challenges with creativity and analytical rigor.
– Laboratory Techniques: Provide hands-on experience in advanced laboratory techniques, instrumentation, and methods relevant to contemporary research in chemistry.
– Communication Skills: Cultivate effective communication skills, both written and oral, to enable students to convey their research findings, ideas, and scientific concepts to diverse audiences.
– Ethical Practices: Emphasize the importance of ethical practices in scientific research and instill a strong sense of integrity in the conduct of experiments and reporting of results.
– Collaboration and Interdisciplinary Skills: Encourage collaboration and interdisciplinary approaches by providing opportunities for students to work with researchers from other fields, fostering a holistic understanding of complex scientific problems.
– Preparation for Ph.D. or Industry Careers: Prepare students for further academic pursuits, such as pursuing a Ph.D., or for careers in industry, where they can apply their knowledge to solve real-world problems.
– Professional Development: Equip students with the tools and skills needed for professional development, including networking, grant writing, and staying current with advancements in the field.
2. Learning Outcomes:
| Symbols | Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs) |
|---|---|
| I. | Knowledge |
| PLO1 | Basic understanding of Philosophy |
| PLO2 | Have basic knowledge of English according to regulations of the Ministry of Education and Training |
| PLO3 | Have basic knowledge of Scientific Research Methods, Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, Advanced Organic Chemistry, Advanced Theoretical Chemistry, Advanced Analytical Chemistry, Nanochemistry and Application, Study Methods for Bioactive Natural Compounds, Green Chemistry – Bioactive Natural Products, Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessments, Management of hazardous solid waste, Analysis of Toxic Chemicals in the Environment, Chemical solutions to adapt and mitigate climate change… |
| PLO4 | Know a deep and advanced understanding of key principles and theories in chemistry and specialized knowledge in their chosen area of concentration. |
| PLO5 | Knowledge and the ability to design, conduct, and analyze original research contribute to the body of knowledge in the field. |
| PLO6 | Know specialized expertise in a particular sub-discipline of chemistry, positioning them as experts in their chosen area. |
| II. | Skills |
| PLO7 | Critical Thinking Skills: Graduates should have honed their critical thinking and analytical skills, enabling them to assess and solve complex problems within the realm of chemistry. |
| PLO8 | Laboratory Proficiency: Graduates should be proficient in advanced laboratory techniques and instrumentation relevant to their field of study. |
| PLO9 | Ability to analyze data and present scientific and technical results. |
| PL010 | Effective Communication: Successful completion of the program implies proficiency in communicating scientific ideas and research findings through well-written reports, publications, and effective oral presentations. |
| PL011 | Professional Development Skills: Acquisition of skills related to professional development, including networking, grant writing, and staying informed about advancements in the field. |
| PL012 | Preparation for Further Study or Employment: Graduates should be well- prepared for either pursuing further academic studies, such as a Ph.D. program, or entering the workforce in industry or research. |
| PL013 | Leadership and Initiative: Graduates may exhibit leadership qualities and the ability to take initiative in research projects, collaborations, or other professional activities. |
| III. | Attitudes |
| PLO14 | Have good moral qualities and a healthy lifestyle. |
| PLO15 | Love your job, be honest and have a high sense of discipline at work. |
| PLO16 | Strictly comply with country laws and regulations of organizations. |
| PLO17 | Have a sense of self-awareness and responsibility towards work, the team, yourself and the community. |
| PLO18 | Have an industrial style and serious working attitude. |
| PLO19 | Have a spirit of community service, integration and international cooperation. |
| PLO20 | Be conscious of self-study, practice and update knowledge. |
| PLO21 | Have a sense of creative thinking. |
| PLO22 | Graduates from the Master’s program in Chemistry will meet the English proficiency according to regulations of the Ministry of Education and Training. |
| PLO23 | Graduates from the Master’s program in Chemistry will meet the basic information technology application level according to Circular No. 03/2014/TT-BTTT dated March 11, 2014 of the Ministry of Information and Communications. |
3. Total knowledge volume of the program:
Total credits for the entire program: 120 ECTS
Breakdown:
- General knowledge: 6 ECTS
- Specialized knowledge: 84 ECTS, where
- Compulsory subjects: 42 ECTS
- Elective subjects: 42 ECTS
- Practice: 12 ECTS, where
- Compulsory subjects: 6 ECTS
- Elective subjects: 6 ECTS
- Graduation Thesis: 18 ECTS
4. List of subjects:
| No. | Code | Name of subject | ECTS |
|---|---|---|---|
| I. GENERAL KNOWLEDGE | 6 | ||
| 1 | 07.043 | Philosophy | 6 |
| II. SPECIALIZED KNOWLEDGE | 84 | ||
| A. Compulsory subjects | 42 | ||
| 1 | HH.04.037 | Advanced Inorganic Chemistry | 6 |
| 2 | HH 04.038 | Advanced Organic Chemistry | 6 |
| 3 | HH 04.040 | Advanced Theoretical Chemistry | 6 |
| 4 | HH 04.034 | Advanced Analytical Chemistry | 6 |
| 5 | HH 04.025 | Coordination Chemistry | 6 |
| 6 | HH 04.036 | Nanochemistry and Application | 6 |
| 7 | HH 04.087 | Physical Chemistry Measurement For Sold Materials | 6 |
| 8 | HH 04.086 | Study Methods for Bioactive Natural Compounds | 6 |
| B. Elective subjects | 42 (42/108) | ||
| 1 | HH 04.044 | Crystal Chemistry | 6 |
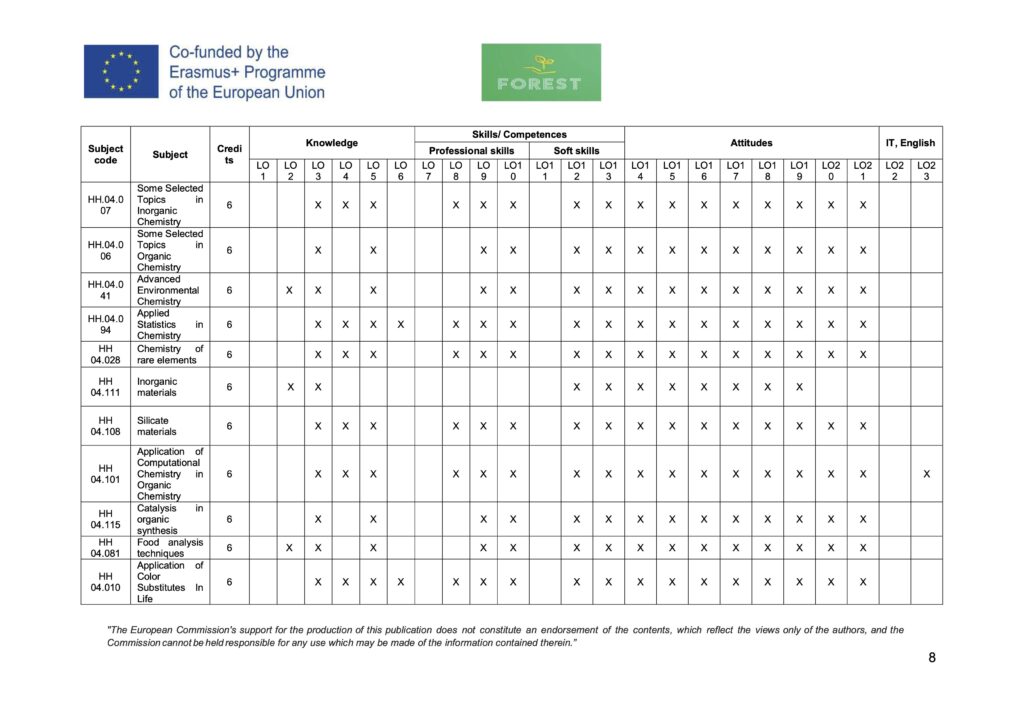
| 2 | HH.04.007 | Some Selected Topics in Inorganic Chemistry | 6 |
| 3 | HH.04.006 | Some Selected Topics in Organic Chemistry | 6 |
| 4 | HH.04.041 | Advanced Environmental Chemistry | 6 |
| 5 | HH.04.094 | Applied Statistics in Chemistry | 6 |
| 6 | HH 04.028 | Chemistry of rare elements | 6 |
| 7 | HH 04.111 | Inorganic materials | 6 |
| 8 | HH 04.108 | Silicate materials | 6 |
| 9 | HH 04.101 | Application of Computational Chemistry in Organic Chemistry | 6 |
| 10 | HH 04.115 | Catalysis in organic synthesis | 6 |
| 11 | HH 04.081 | Food analysis techniques | 6 |
| 12 | HH 04.010 | Application of Color Substitutes In Life | 6 |
| 13 | HH 04.051 | Separation and Enrichment Techniques | 6 |
| 14 | HH 04.128 | Green Chemistry – Bioactive Natural Products | 6 |
| 15 | HH 04.129 | Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessments | 6 |
| 16 | HH 04.130 | Management of hazardous solid waste | 6 |
| 17 | HH 04.131 | Analysis of Toxic Chemicals in the Environment | 6 |
| 18 | HH 04.132 | Chemical solutions to adapt and mitigate climate change | 6 |
| III. PRACTICE | 12 | ||
| A. Compulsory subjects | 6 | ||
| 1 | HH 04.078 | Practice 1: Modern Spectrophotometric Analysis | 6 |
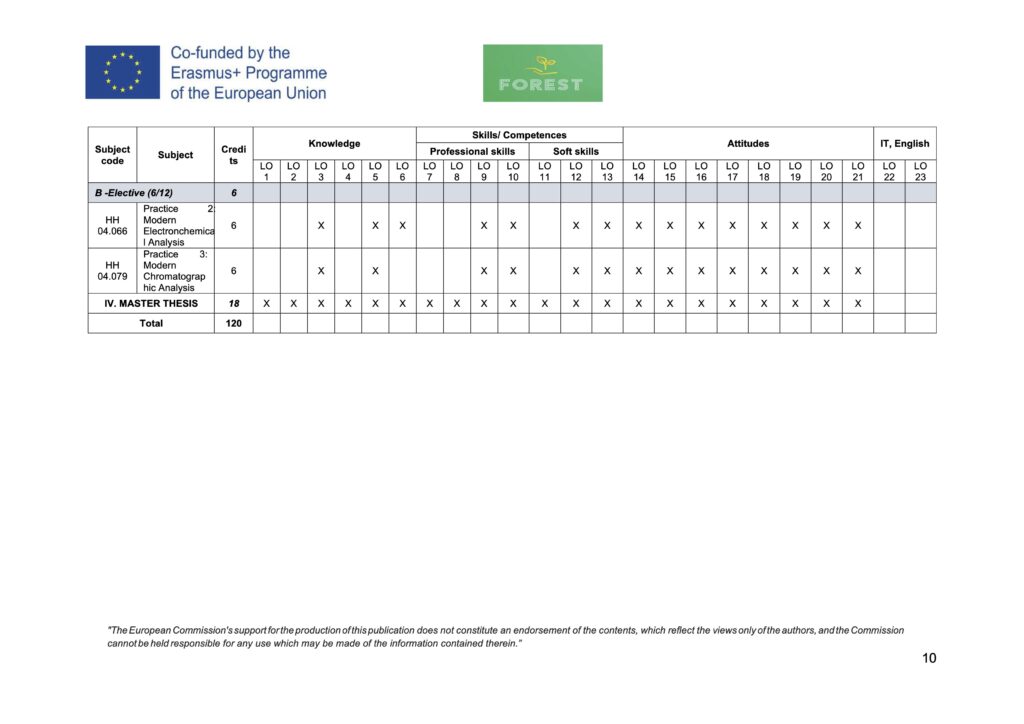
| B. Elective subjects | 6 (6/12) | ||
| 1 | HH 04.066 | Practice 2: Modern Electronchemical Analysis | 6 |
| 2 | HH 04.079 | Practice 3: Modern Chromatographic Analysis | 6 |
| IV. MASTER’S THESIS | 18 | ||
| TOTAL ECTS | 120 |


6. Brief description and workload of the subjects
6.1 Philosophy (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: The subject consists of four topics: Chapter 1 covers characteristics of Western philosophy, Eastern philosophy (including Vietnamese philosophical thought at a basic level), and Marxist philosophy. Chapter 2 explores advanced topics related to Marxist-Leninist philosophy in the current stage and its worldview, methodology, and global role. Chapter 3 delves into the interrelation between philosophy and various sciences, emphasizing the role of worldview and methodology in the development of science and in the perception, teaching, and research of subjects in the natural sciences and technology field. Chapter 4 analyzes issues regarding the role of sciences in societal life.
6.2. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: The module provides students with advanced knowledge of inorganic chemistry theory to solve several problems related to the chemistry of inorganic substances and inorganic reactions including heat. Kinetics in inorganic chemistry, redox reactions, acid and base reactions.
6.3. Advanced Organic Chemistry (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: The content includes the following main basic knowledge: The nature of bonds in organic compounds; Spatial structure of organic compounds; Relationship between properties and structures of organic compounds; Organic reactions: types of reactions, reactants and reaction mechanisms.
6.4. Advanced Theoretical Chemistry (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: This module includes advanced knowledge about applying the principles of thermodynamics to chemical equilibrium research and phase equilibrium research. Chemical kinetics research methods and experimental data processing. Theory of elementary processes. Research on electrochemical kinetics. Research on statistical thermodynamics and thermodynamics of non-equilibrium processes.
6.5. Advanced Analytical Chemistry (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: This module introduces advanced knowledge about calculating ion balance in solutions, quantifying substances using volumetric analysis, and basic knowledge about ensuring analytical quality. Additionally, students develop scientific reasoning skills and proficiency in using specialized English.
6.6. Coordination Chemistry (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: The module provides students with knowledge about coordination compounds (complexes) including basic concepts of complexes, the role of complexes in life and industry, nomenclature and isomerism of complexes, methods of synthesizing complexes, methods of determining the composition of complexes and methods of analyzing the structure of complexes.
6.7. Nanochemistry and Application (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: Introduction to physicochemical properties of solid surfaces, nanostructures and zero-dimensional, one-dimensional, and two-dimensional nanomaterials. Technologies for manufacturing nanomaterials such as physical vapor phase deposition, chemical atomic layer deposition, electrochemical deposition, self-joining, etc. Structural characterization methods such as XRD, SAXS, SEM, TEM, SPM, BET, chemical characteristics such as optical, electronic, ion spectra, etc. Applications of nanomaterials.
6.8. Physical Chemistry Measurement For Solid Materials (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: Introducing methods of analyzing the structure of inorganic materials: electron absorption spectrum, nuclear magnetic resonance, mass, infrared, X-ray diffraction, thermal analysis, electron microscopy; Apply these methods in studying material structure.
6.9. Study Methods for Bioactive Natural Compounds (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: The module equips students with basic knowledge about natural compounds: origin, methods of isolation, purification, structure determination and biological activity; Basic theory on chemical structure, biological activity and applications of some groups of natural compounds being used as medicines, functional foods, and agricultural products: flavonoids, compounds containing nitrogen, terpenoids, steroids and some other groups of natural compounds.
6.10. Crystal Chemistry (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: This module offers foundational knowledge on crystallography, the structure of solids in crystalline and amorphous states, phase transitions in solids, fundamental characteristics of solid-state reactions (thermodynamics, kinetics mechanisms, and dynamic models), and various methods for synthesizing solids (materials) and their applications in the production of inorganic compounds and materials. Additionally, the course provides insights into structural analysis methods and the relationship between structure and certain properties (optical, electrical, magnetic, etc.) of solids.
6.11. Some Selected Topics in Inorganic Chemistry (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: Introducing methods of analyzing the structure of inorganic materials: electron absorption spectrum, nuclear magnetic resonance, mass, infrared, X-ray diffraction, thermal analysis, electron microscopy; Apply these methods in studying material structure.
6.12. Some Selected Topics in Organic Chemistry (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: This module includes: Nomenclature and spatial structure of organic compounds; Stereochemistry, chemical selectivity: agents, reactions; and Pericyclic reactions.
6.13. Advanced Environmental Chemistry (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: This module covers the following contents: Global environmental issues: acid rain, greenhouse effect and climate change, ozone layer depletion and the ozone hole, persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the environment: causes, impacts, and control solutions. Method for rapid assessment of water, air, and soil environmental pollution sources: determine the pollution load from wastewater sources, exhaust gases, and solid waste emitted into the environment. Water quality assessment method based on the Water Quality Index (WQI): approach to building and using WQI, WQI model of the Sanitation Foundation of the US, Canada, and India…
6.14. Applied Statistics in Chemistry (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: This module introduces the application of quantities and statistical tools to process, check, and evaluate experimental results; consider correlation and regression; and Experimental planning (variance analysis, modeling, and optimization of experiments) in chemical research. Students are also introduced to applying statistical software (stratigraphic 7.0, Minitab, or SPSS) to solve related research problems.
6.15. Chemistry of rare elements (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: The module provides students with advanced knowledge of the chemistry of rare earth elements and ore processing methods; refined; extraction; cup; division and acquisition of rare earth elements. Application of rare elements in the fields of science, technology and life.
6.16. Inorganic materials (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: The module provides students with some advanced knowledge about the production process of some common inorganic materials.
6.17. Silicate materials (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: The module “Silicate materials” introduces basic raw materials to produce Portland cement (limestone, clay, iron ore); Portland cement production techniques (calculation of mixing ratio, clinker smelting process, clinker grinding); additives for cement; Curing process of Portland cement; Concrete corrosion and concrete protection measures. Introduction to basic raw materials for ceramic production (kaolin, clay, feldspar, quartz sand); ceramic production techniques (calculating material proportions, processing materials, shaping products, drying, firing, glazing); pigments for ceramics and some types of pigments commonly used in ceramic production.
6.18. Application of Computational Chemistry in Organic Chemistry (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: This module uses software Gaussian 09, Spartan, AIM2000, NBO6, VASP… to calculate thermodynamic quantities of organic compounds: Bond strength, Electron affinity, Calculate and simulate spectra applied in Organic chemistry: IR spectrum, NMR, Raman… Research the reaction mechanism, study the kinetics of the reaction and influencing factors, study the antioxidant activity of organic compounds, and study the simulation of biological activity using appropriate simulation methods. synthesis and orientation of organic synthesis using simulation methods.
6.19. Catalysis in organic synthesis (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: This module includes: Theory of catalysis, physical and chemical bases of catalysis including Catalytic research methods and Catalysis in the oil processing industry.
6.20. Food analysis techniques (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: This module provides knowledge about the chemical composition of food: glucose, protein, lipid, vitamins; Ingredients related to food safety: products formed due to metabolism during food preservation, ingredients related to raw material sources: heavy metals, residues of plant protection chemicals… food processing process.
6.21. Application of Color Substitutes in Life (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: This module includes the theory of color compounds: concepts of colorants, dyes, and pigments; Some important families of color compounds and dyes; Analyzing and evaluating dyes and color compounds; and Colorants in classical photography and electronic photography, in ink and printing, in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, in analysis and the environment…
6.22. Separation and Enrichment Techniques (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: This module introduces several separation and enrichment methods such as Liquid-liquid extraction, solid phase extraction, precipitation, and distillation… commonly used in substance analysis. Each method presents principles, content, influencing factors, etc., as well as calculation exercises related to the method.
6.23. Green Chemistry – Bioactive Natural Products (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: The module provides students with the concept and classification of biologically active natural compounds: terpenoids, steroids, phenolic compounds and flavonoids, alkaloids, carbohydrates, etc. At the same time, it helps students gain knowledge about density functional theory, molecular docking simulation, and application of algorithms and calculation methods to solve the nature of bonds, structure, and properties. properties, relationships between structure – properties, structure – activity of natural compounds. Provide knowledge about using computational software to predict the physical and chemical properties of natural compounds. Apply knowledge to solve problems in scientific research and practice.
6.24. Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessments (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: The module provides students with basic knowledge about the pollution of toxic chemicals such as POPs, trace elements and microplastics in different environmental objects. And provide tools and methods to assess risks to ecosystems and human health.
6.25. Management of hazardous solid waste (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: The module provides students with an overview of the characteristics of hazardous waste, processes and principles for storing, transporting, treating and safely disposing of hazardous waste. Topics/concepts including programs, regulations, hazards and methods related to hazardous waste management in household, business, agriculture and industry are also introduced to help students Identify, describe and compare them in developing and developed countries.
6.26. Analysis of Toxic Chemicals in the Environment (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: The module provides students with basic knowledge about toxic chemicals (POPs, trace elements and microplastics) in the environment, the causes and modern analytical methods to analyze them.
6.27. Chemical solutions to adapt and mitigate climate change (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: The module provides students with basic knowledge about climate and climate change, the causes and solutions to adapt to climate change and mitigate the impact of climate change. climate change to humans and nature and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
6.28. Practice 1: Modern Spectrophotometric Analysis (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: Principles of spectrum generation, principle diagram of spectrometer structure, correlation between molecular structure atoms and spectra. Analyzing the spectra and determining the structural formula of the organic compound. Application of spectroscopic methods in the fields of organic compound research.
6.29. Practice 2: Modern Electrochemical Analysis (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: This module introduces modern electrochemical analysis methods: theory and practice: Potential measurement method using ion selective electrodes and applications in practical analysis; Modern polar spectroscopy methods (differential pulse spectroscopy, square wave spectroscopy) and their applications in inorganic and organic analysis; Anodic Stripping Voltammetry and Adsorptive Stripping Voltammetry and application in trace analysis; Cyclic Voltammetry method.
6.30. Practice 3: Modern Chromatographic Analysis (6 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 6 (1/1/4)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: Principles and pratising of analysis up to the determination of the structure of a substance. Some sample analysis methods are applied on actual samples, how to choose analysis methods and process analysis results for some unknown compounds and unknown compounds.
6.31. Master Thesis (30 ECTS):
Learning time allocation: 30 (0/10/20)
Subject prerequisite: None
Previous subject: None
Summary: In this master thesis, students are tasked with addressing a scientific and technical by using various methods. This involves defining the scope of a topic, developing a research methodology, conducting the research, collecting data, and analyzing and synthesizing the data to discover a scientific and technical pattern in the field of Chemistry. Ultimately, students are required to interpret the research results clearly and logically through both written and verbal communication.